The system that collects and processes transaction-data and disseminates financial information to interested parties is known as the accounting system or accounting information system.
This system includes every step of the accounting cycle. It also includes documentary evidence of transactions. Therefore, the transaction with documentary evidence, journal, ledger, trial balance, worksheet, financial statements determining results, etc. are included in the accounting information system.
Recording of a business transaction, ledger preparation, trial balance preparation, analyzing the process of financial Statements are similar in all business organizations. The speed and efficiency of the system depend on accounting information systems in practice.
For example, a student decides to go home after attending an accounting class. His roads to his home are two-one is side road and the other is a superhighway.
Now it is up to the student which road he will take to go home. But his intention is one i.e. to reach home.
He can go home driving a car using either of the roads. But it is expected that he will drive the car to go home by the super highway because this road is very much speedy.
It is also true in case of an accounting information system. If a particular accounting system is comparatively speedy and efficient, it can be used for the accounting process.
In this stage identification of various accounting systems and their characteristics will be discussed.
Processing transactions through a general journal and general ledger manually is one type of accounting system.
Another accounting system is to add a special journal and subsidiary ledger to the above-mentioned system.
Accounts keeping through machine i.e. computer can be done more speedily and efficiently in comparison to manual operating of accounting activities.
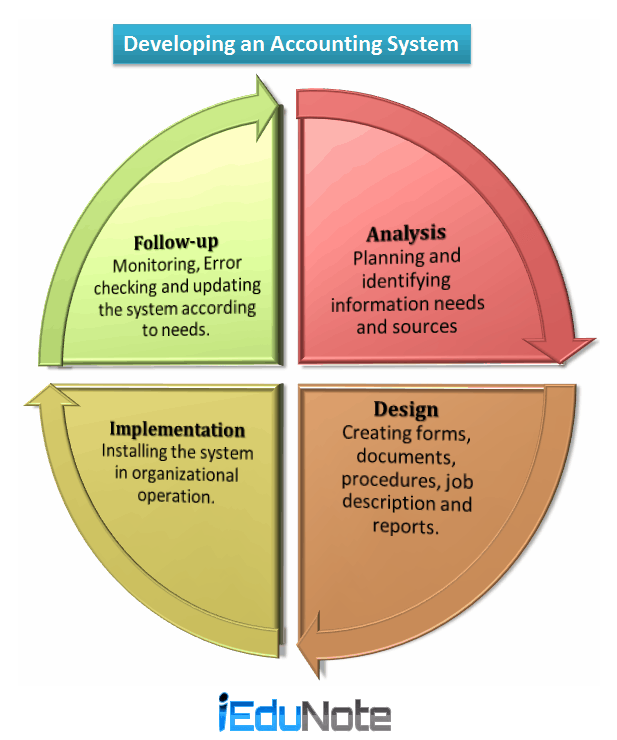
Developing an Accounting System
An ideal accounting system does not come into force automatically. It is to be very much carefully planned, designed, arranged, managed and modified.
In developing an ideal accounting system the following four steps are necessary;
- Analysis.
- Design.
- Implementation.
- Follow-up.
Analysis
At first, it is to be ascertained what information is necessary for internal and external users. An information analyst is to identify sources of the necessary information for collecting data and prepare reports and preserve them properly.
Strength and weakness of an existing information system are to be identified for its analysis.
Design
For formulating a new accounting system designing of forms and documents, sorting of the method and working process, preparing a statement of work, collecting techniques of control, preparing reports and selecting equipment are necessary.
Slight changes are required for redesigning existing accounting information system.
Implementation
For the implementation of a new or modified accounting information system, necessary documentary evidence of information, the process of methods and installation of necessary equipment, etc. are to be activated.
Employees concerned are to be given training and they are to be monitored closely.
Follow-up
After the implementation of the accounting information system and making it workable, its weakness and breakdown are to be monitored very closely and its effectiveness and design are to be compared with organizational objectives.
If needed changes are to be brought in its implementation process of design. The above-mentioned steps represent the life cycle of an accounting information system. This suggests that some accounting information systems are always unchangeable.
But the expansion of knowledge, experience and technology and occurrence of organizational changes might create and change the accounting information system.