Unlock the transformative power of learning. Explore principles, theories, and components to shape behavior and expand knowledge for personal growth.
Definition of Learning
Learning is described as the process of having one’s behavior modified, more or less permanently, by what he does and the consequences of his action, or by what he observes. It is a process by which an activity originates or is changed through responding to a situation. Learning involves change.
Change may be good or bad from the organizational point of view. People can learn unfavorable or favorable behavior. It is the expansion of what one may already know or perceive.
It is the accumulation of knowledge but, more importantly, the application of this knowledge. It does not happen all at once but builds upon and is shaped by previous knowledge.
To that end, learning may be viewed as a process rather than a collection of factual and procedural knowledge.
Learning produces changes in the organism, and the changes produced are relatively permanent. If one cannot use newly acquired information for his/her practical use or benefit, then it is doubtful that he/she is engaged in the learning process.
Learning means behavioral modification, especially through experience or conditioning.
- Steers and Porter defined learning as “relatively permanent change in behavior potentiality that results from reinforced practice or experience.
- Hulse, Deese, and Egeth defined learning as “relatively permanent change in behavior or potential behavior that results from direct or indirect experience.”
- According to S.P. Robbins, “Learning is any relatively permanent change in behavior resulting from experience.”
- According to Scott Miller, “Learning is a change that occurs in response to thinking or other sensual stimuli.”
- According to S. P. Robbins, “Learning is any relatively permanent change in behavior resulting from experience.”
- According to Biswanath Ghosh, “Learning is the modification of behavior through experience and training.”
- According to Michele Griffin, “Learning is a stance taken by an individual that allows for the acquisition of information, attitudes, and practices, through observation, seeking previous knowledge, searching out guides, and looking within as well as without.
- Michael L. Ray defines learning as the more or less permanent acquisition of tendencies to behave in particular ways in response to particular situations or stimuli.
Learning may be defined as a relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs due to prior experience.
When we observe any change in a person’s behavior, we can say that learning has taken place. Learning means the act, process, or experience of gaining knowledge or skill.
It can change our behavior. By birth, every people learned from his environment.
On the other hand, knowledge or skill gained through schooling or study is also called learning.
Finally, we can say that learning has taken place if individuals behave, react, and respond taken from others as a result of experiences change in behavior.
Characteristics of Learning

Learning is the process by which one acquires, ingests, and stores or accepts information. Our experiences with learned information compose our bodies of knowledge. Learning is a process unique to each individual.
There are some characteristics of learning.
- Learning involves change.
- All learning involves activities.
- Learning Requires Interaction.
- Constitute Learning.
- Learning is a Lifelong Process.
- Learning Occurs Randomly Throughout Life.
- Learning Involves Problems Solving.
- Learning is the Process of Acquiring Information.
- Learning Involves far more than Thinking.
- Experience is Necessary for Learning.
Learn more about the Characteristics of Learning.
Principles of Learning
Learning principles are guidelines for how people learn most effectively. The more these principles are reflected in training, and the more effective training is likely to be.
Research suggests that they apply equally to domestic and international situations. These are the basic principles or conditions that facilitate learning.
- Participation.
- Repetition.
- Relevance.
- Transference.
- Feedback.
Guidelines for Learning
The guidelines for learning are known as principles of learning. The principles of learning are theoretical statements summarizing decades of learning research.
By summarizing these, we can know about the following guidelines of learning;
- Readiness.
- Recency.
- Repetitiveness.
- Reinforcement.
- Relevance.
- Feedback.
- Schedules of Learning.
- Whole vs. Part Learning.
- Primacy.
- Boundary Less.
- Presentation Effect.
- Multiples Routes.
You must understand how learning principles impact learning.
Theories of Learning

Learning is the individual growth of the person as a result of cooperative interaction with others. It is the advancement of understanding that enables the learner to function better in their environment, improve and adapt behaviors, create and maintain healthy relationships, and achieve personal success.
Learning has taken place if an individual behaves, reacts, and responds taken from others due to experiences change in behavior or formerly behave.
There are several theories of learning;
- Classical Conditioning
- Operant Conditioning
- Cognitive Theory.
- Social Learning Theory.
Know more about theories of learning.
Components of Learning
Learning has taken place if an individual behaves, reacts, and responds in a way taken from others as a result of experiences.
Learning can be defined as the relatively permanent change in behavior potentiality that results from reinforced practice or experience. It can change our behavior.
By birth, every people learned from his environment.
On the other hand, knowledge or skill gained through schooling or study is also called learning. Learning has many components.
These components are given below:
- Learning involves change. Change may sound good or bad from an organizational point of view. People can learn unfavorable behaviors to hold prejudices or to restrict their output.
- The change must be ingrained. Temporary changes may be only reflexive and may not represent learning. Therefore the requirement that learning must be relatively permanent.
- Some form of experience is necessary for learning. Experience may be acquired directly through observation or practice, or it may be acquired indirectly through reading.
- Learning involves concentration and participation. It usually is quicker and long-lasting when the learner participates actively. As a result of participation, people learn more quickly and retain that learning longer.
These are just a few of all the components of learning.
Barriers to Learning

Barriers to learning are problems or situations that prevent learners from accessing programs, make it difficult for learners to go to class, or make it hard for learners to concentrate and learn.
- Presentation problem.
- Another barrier to learning is changing the expectation of a new culture.
- Learners do not get appropriate support.
- Employment-related issues.
- Sometimes employees cannot concentrate properly.
- The financial problem can be a barrier to learning.
- Political influence can be a barrier.
Understand how these barriers to learning influence the learning process.
Overcoming Learning Barriers

Knowledge or skill gained through schooling or study is also called learning. In learning, every learner has to face some barriers which have to overcome by the learner himself.
Otherwise, they stumble while processing information, taking longer to grasp the concept of requiring numerous exposures over a sustained period.
To overcome the barriers, learners have to make changes in the ways of learning.
- Environment.
- Routine.
- Verbal Instructions.
- Respect.
- Non-curricular Activities.
- Improving Communication Skills.
- Giving ICT and Presentation Facilities.
- Give Concentration.
- Learn the New Culture before Going There.
- Provide Effective and Timely Feedback.
See how these help in overcoming learning barriers.
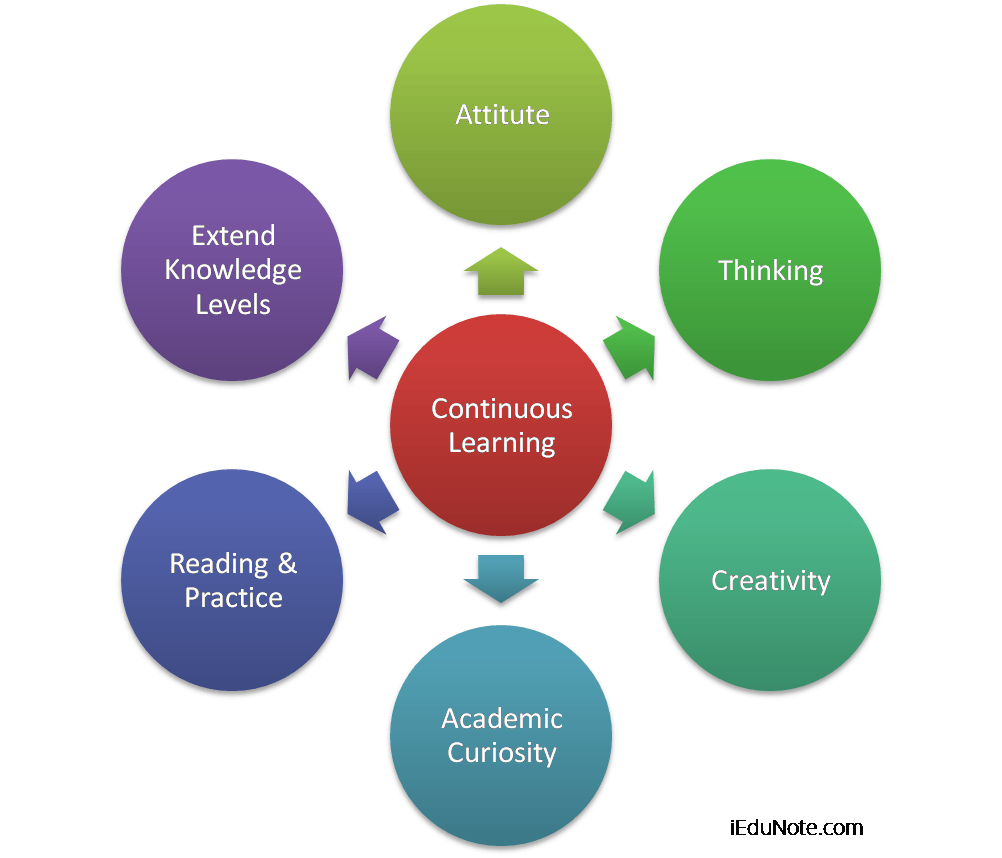
Learning is the Continuous Process
Learning is a continuous process of life, the pinnacle of the attitude and vision of the universe. Learning is the only thing that distinguishes humans from animals. Being a human, we have a great privilege to think. Thinking is a great thing we all can do.
Conclusion
Learning gives creativity; creativity leads to thinking; thinking provides knowledge; knowledge makes you great. The learning process is not rigid, and it is continuously happening. It shapes our behavior and perspective of the world.
Therefore, please let us not limit learning just to a subject. If we can see it with a wide range of thinking, then the whole world looks very small.