Growth is one of the most discussed and lauded strategic options. It is equated with managerial success and achievement.
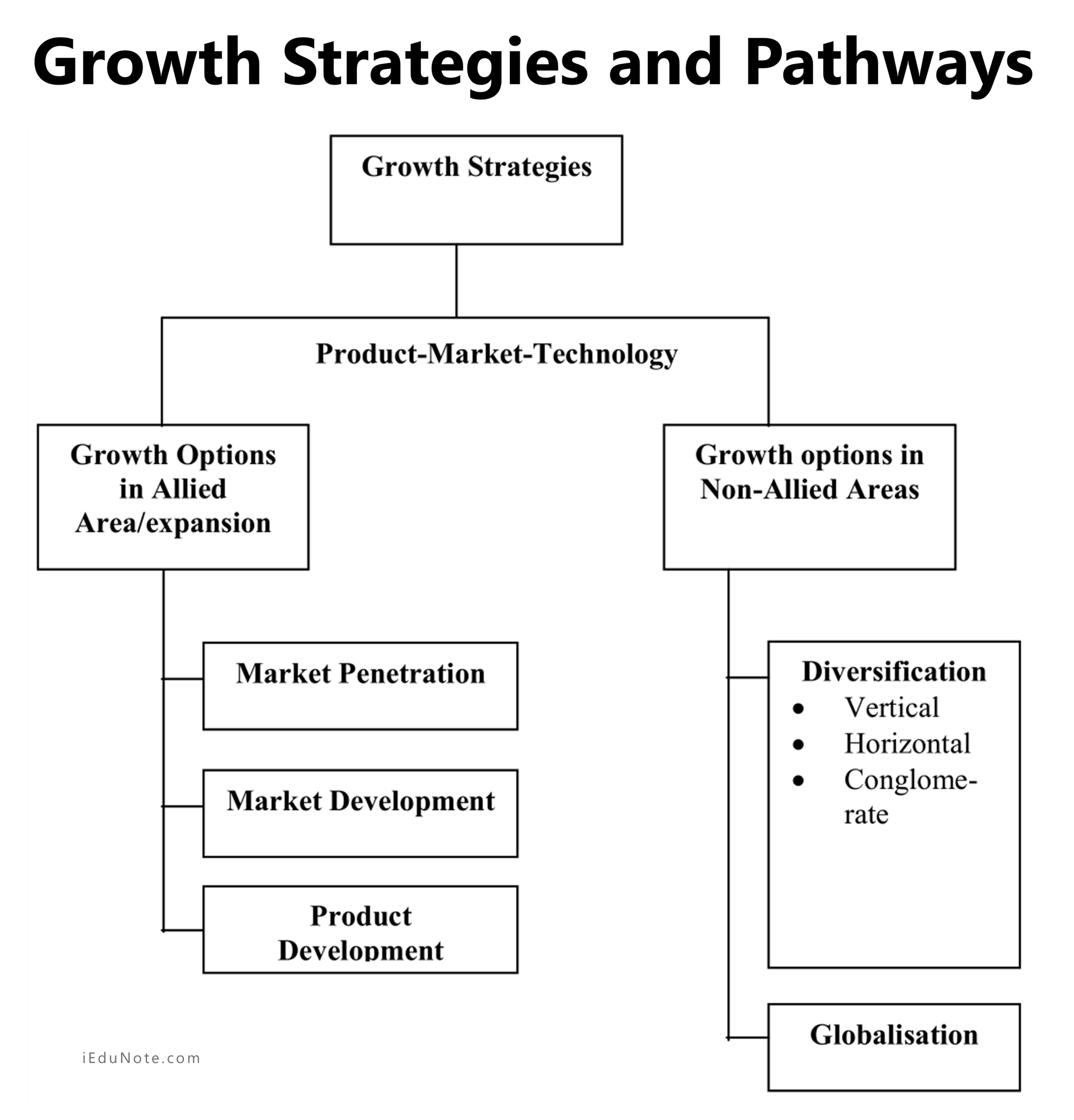
An organization may grow by expansion (when it concentrates within a broad allied product market scope). Technology plays an essential underlying role in growth in today’s context.
It enables companies to design, develop, and manufacture better products. Communication technology also enables the organization to meet unserved needs in unreached markets.
Alternatively, an organization may grow beyond its product market scope.
The organization can move into new markets, and offer products that are different from its present ones based on new technology and manufacturing (the organization explores a new line of business).
It can even tap overseas markets for the same new or differentiated products (diversification). A company may adopt a growth strategy when it wants to expand its market and thereby improve profitability.
Usually, this strategy is undertaken when a company has enough resources to expand the business and is capable of managing the new risks involved with expansion.
A company may adopt a growth strategy when it wants to expand its market and thereby improve profitability.
Usually, this strategy is undertaken when a company has enough resources to expand the business and is capable of managing the new risks involved with expansion.
Ways for Implementing a Growth Strategy
A growth strategy can be implemented in various ways. It can usually be implemented through:
- Internal growth (using own resources).
- Acquisition (one company purchases assets of another company and absorbs them into its operations).
- Merger (two or more companies combine into one company).
- Joint Ventures (two or more organizations pool their resources for a given project or business product on a temporary or permanent basis).
- Horizontal Integration (Adding one or more businesses that produce similar products, usually buying another organization in the same business)