7 types of journal books are maintained in accounting for the convenient keeping of accounts and recording transactions of similar nature. Under the double-entry system, there are mainly 7 different types of journal in accounting. Transactions are primarily recorded in the journal and thereafter posted to the ledger.
It is difficult to find out effects and information relating to the transaction if all the transactions are recorded in a single journal. Recording of all transactions in one general journal is a time consuming, laborious and troublesome task.
That is why in modem times the use of many journals instead of one journal has been introduced in almost all business concerns, especially the medium and large size business concerns.
For convenient keeping of accounts, maintaining more than one special journal according to the nature of transactions instead of one journal is called classification of the journal.
The transactions of the same nature are recorded in a special journal. These are termed as a daily journal, subsidiary journal or special journal.
Most large size business concerns record particular transactions in special journal, side by side general journal.

7 Types of Journals in Accounting
Here it should be mentioned that most of the business organizations of our country are of small or medium size. These organizations maintain cash book for recording daily cash receipts and cash payments instead of maintaining cash receipt journal and cash payment journal separately.
But where cash receipts journal and cash payments journal are maintained cash book is not needed.
Purchase Journal
The special journal used for recording the credit purchase of merchandise is called a purchase journal.
In purchase journal transactions of merchandise purchased on credit for sale are recorded. An asset purchased on the account is not recorded in the purchase journal.
But many are of the opinion to record all credit transactions in the multi-column purchase journal.
For instance, Pyle and Larson have shown credit purchase of assets and supplies, etc. in a purchase journal under a separate column – debiting asset or office supplies and crediting accounts payable.
Since purchase journal is meant for recording merchandise purchased on credit purchase of assets and other things on credit should not be recorded in the purchase journal rather a recording of these in general journal is more acceptable.
The format of the purchase journal:
Single-column purchase journal:
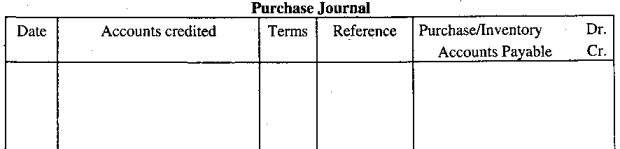
A single-column purchase journal is used only for recording credit purchase of merchandise. In this respect, the format of the purchase journal under periodic and perpetual systems is the same.
But in the case of periodic system purchase account and in the case of the perpetual system merchandise inventory accounts are debited and account payable is credited in both the cases:
Multi-column purchase journal
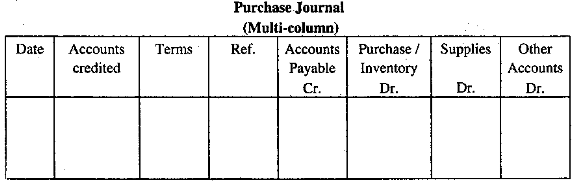
Some organizations use a multi-column purchase journal wherein credit purchase of merchandise, assets and other things are recorded. Organizations concerned use columns of the journal according to their needs.
Trade discount
At the time of sale, the value which is exempted from catalog price as per terms by the seller to the purchaser is called trade discount.
The trade discount is allowed in order to give benefit to the buyer of goods so that he can earn a definite amount of profit by selling goods. For example, at the time of price fixing the price of a commodity is fixed at $100 including a 5% trade discount.
At the time of selling the seller can sell this commodity granting a 5% trade discount i.e. the buyer gets the benefit to sell the commodity at $95. Trade discount is not recorded in the books of account because it does not bring any financial change of seller or buyer.
Only in the invoice, the trade discount is shown by way of deduction from the invoice price. In purchase and sale books/journals the net purchase or sale value after deducting trade discount from the total value of goods is shown.
In both, cases i.e. in cash sale or credit sale trade discount is generally allowed.
Posting in Ledger
The purchase journal is not written in accordance with a double-entry system i.e., it is not written determining the debit account and credit account.
So, at the time of posting in the ledger, its dual aspects are to be completed. It is not mandatory to show the journal entry which is submitted at the end of the purchase journal.
For convenient postings in the ledger, these journals have been given. Opening purchase account in the ledger the weekly or monthly purchase is to be debited from the miscellaneous account in its debit side.
Opening an individual account in the name of creditor or creditors recorded in the purchase journal respective receivable amounts are credited to the credit side.
Balancing ledger accounts is not generally determined or shown until the end of the year, because posting in these accounts may be needed throughout the whole year.
Sales Journal
Sales journal is used for recording the credit sale of merchandise only.
Cash sale of merchandise is recorded in the cash receipt journal. A credit sale of an asset is recorded in general journal.
Cash Receipts Journal
The special journal used for recording all types of cash receipts is called the cash receipts journal.
In modem age, the introduction of cash receipts journal is in practice in medium and large size business organizations.
All kinds, of cash receipts, are recorded in this journal. The main sources of cash receipts are two; Cash from cash sale and cash from accounts receivable.
There might have other sources of cash receipts. For example, taking a loan from a bank, interest receipts, the cash sale of assets, etc.
Since the cash book does not contain a separate required column for recording cash receipts, it fails to provide information regarding various cash receipts and cash flow.
To overcome these entire limitations multi-column cash receipts journal is required.
Generally in the cash receipts journal to debit columns for cash receipts and cash discount and three credit columns for accounts receivable, sales and other accounts are there. Cash received from various sources other than cash sales and account receivables are recorded in other accounts column.
If the perpetual inventory system is followed in recording merchandise inventory, a separate journal entry is passed along with a sale journal where the cost of goods sold is debited and merchandise inventory is credited.
It may be mentioned that under the periodic inventory system this additional journal entry is not required.
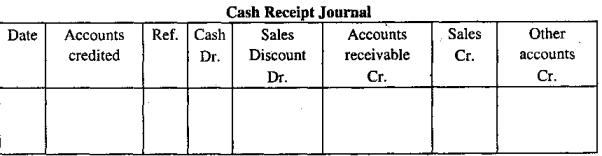
Periodic Inventory System: Under periodic inventory system the format of cash receipt journal is as follows:
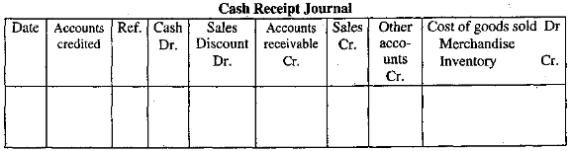
Perpetual Inventory System: Under the perpetual inventory system the format of cash receipt journal is as follows:
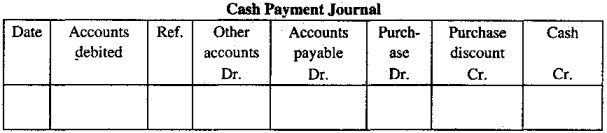
Cash Payment Journal
The; special journal used for recording various transactions relating to cash payment is called a cash payment journal. Business concerns usually pay debts by cheques.
Payment by cheque is treated as a cash payment.
For the acceptability of cash payment, business organizations pay bills by cheques. The cash payment journal contains many money columns as cash payments are made under many heads.
Payment to accounts payable is an important item among the cash payment items and for this account payable provision for a separate debit, the money column is made in cash payment journal.
As purchase discount arises with various payments a separate purchase discount credit money column is kept in it. A cash credit column is provided for cash payment and cheque payment.
Another debit column for office supplies is also contained in the cash payment journal. Besides, for showing other payment there contains another accounts-debit column. A format of the multi-column cash payments journal is shown below:
Purchase Return Journal
The special journal, where purchase returns of credit purchase are recorded, is called a purchase return journal.
In the case of isolation of purchase agreement or in the case of defective goods the purchaser returns the- goods to the seller. While returning goods to the seller a slip containing reasons for the return of goods is sent along with goods.
This is called a debit note. The seller also sends a note to the purchaser as a reply which is called a credit note. It may be mentioned that goods purchased on cash if returned are not recorded in the purchase return journal.
A format of purchase return journal is shown below:

Sales Return Journal
The special journal, where the credit sale returns are recorded, is called a sales return journal. The sales return journal is prepared from debit notes sent by the buyer with returned goods. In reply, the seller sends a credit note.
The format of sales return is similar to that of sales journal excepting challan/invoice column where credit note is written.
It may be mentioned that where the sales return transactions are large in number this sales return journal is maintained.
But where such return transactions are very few in number, these are recorded in the general journal.
Journal Proper
The transactions other than the transactions recorded in cash receipts journal, cash payment special, purchase journal, sales journal, etc. are recorded in journal proper or general journal.
For example;
Purchase of assets on credit, the stock of goods at the year-end, rectification of errors, adjustment of accounts, etc. are recorded in journal proper.
Therefore, the journal, wherein the transactions which cannot be directly recorded in a particular journal are recorded, is called journal proper.
In the journal proper generally, the following transaction is recorded;
- Opening Entry: The journal entry which is passed at the beginning of the current year for recording assets and liabilities of the previous year is called opening entry.
- Closing Entry: The journal entries, which are passed to close the periodical expenses and income transferring them to the income statement, are called closing entries. That is all income – expense accounts, sales-purchase accounts, and profit- loss accounts are closed through transfer to the income statement.
- Adjustment Entry: The journal entry through which accrued expenses and income and advance income, expenses, depreciation, specific provisions, etc. are adjusted is called adjustment entry.
- Rectification Entry: The entry, through which errors in accounts are rectified, is called rectification entry.
- Transfer Entry: The entry which is made for transferring fund from one account to another account is called transfer entry.
- Credit Purchase and Sale of Assets: The entry which is needed for recording transactions relating to credit purchase and sale of assets is called credit purchase and sale of assets entry. For example, Furniture purchased from Sonargaon Furniture for $5,000.
- Other Entry: Entries that cannot be recorded in another journal.