In Unit banking, the banking operations are carried on through a single office rather than through a network of branches under the control of a single bank. The single office is both the controlling and the operating unit. Each banking unit is a separate company with a separate entity, with its capital, shareholders, and board of directors.
Unit banking is a system of banking under which a single banking organization provides banking services. Such a bank has a single office or place of work. It has its own governing body or board of directors.
The area of operations and the bank size is small under the unit banking system compared to the branch banking system. However, a few unit banks may have branches operating in a limited area; thus, it is a localized banking system.
Advantages of Unit Banking
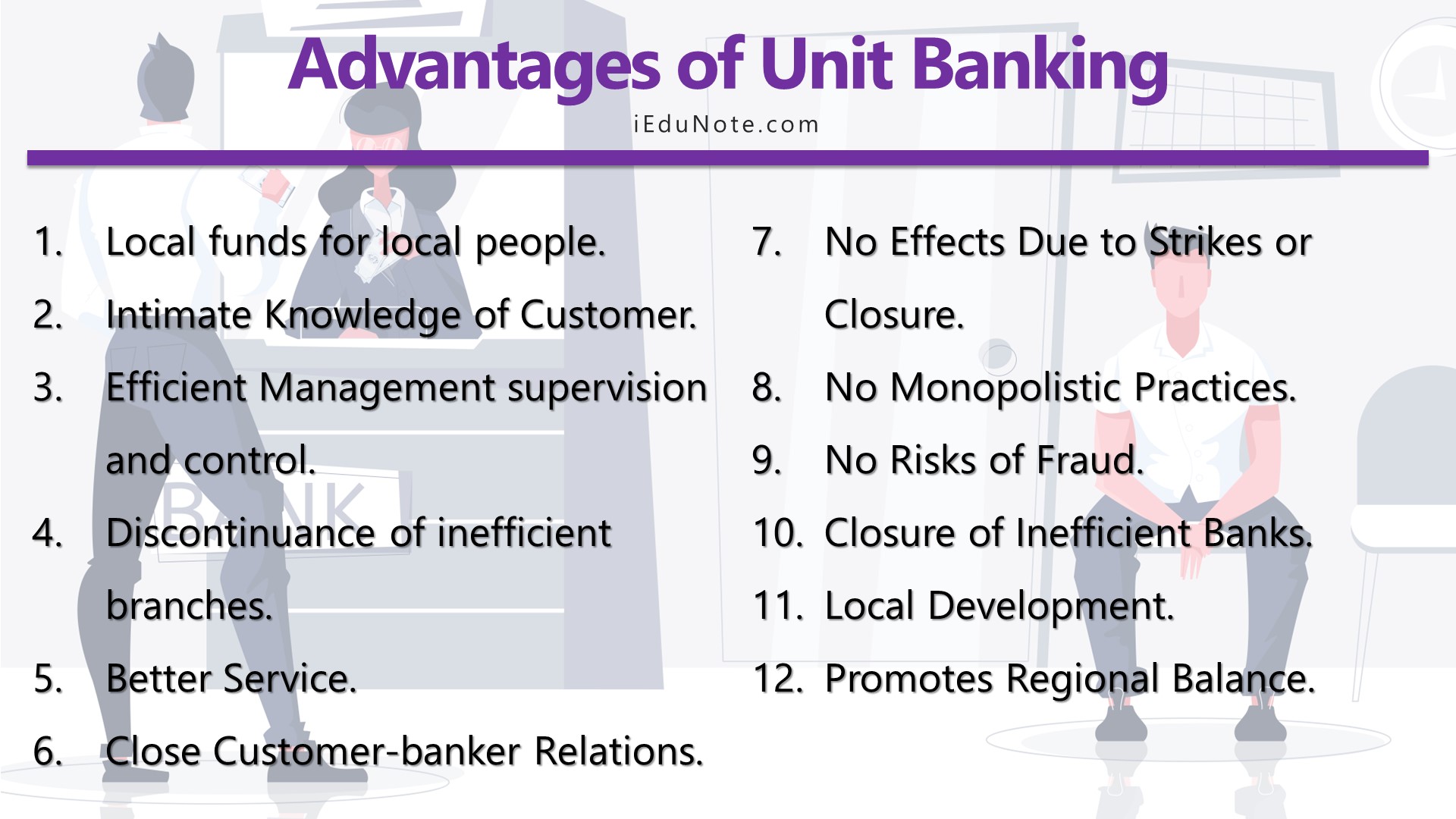
12 advantages of the unit banking system are;
- Local funds for local people.
- Intimate Knowledge of Customer.
- Efficient Management supervision and control.
- Discontinuance of inefficient branches.
- Better Service.
- Close Customer-banker Relations.
- No Effects Due to Strikes or Closure.
- No Monopolistic Practices.
- No Risks of Fraud.
- Closure of Inefficient Banks.
- Local Development.
- Promotes Regional Balance.
Let’s see how the unit banking system is advantageous for the economy and local population.
1. Local funds for local people
The unit banking of a particular locality utilizes its resources to develop its locality only and does not transfer them to other localities like branch banking.
2. Intimate Knowledge of the Customer
The Managers of the local unit bank can easily acquire the personal knowledge of customers and the specialized knowledge of the local industries and occupations.
Therefore, he is better positioned to serve the local borrowers’ needs; lie has greater chances of cultivating a friendly and personal relationship with the individual entrepreneurs of his locality.
3. Efficient Management supervision and control
One of the most important advantages of the unit banking system is that it can be managed efficiently because of its size and work. Coordination and control become effective.
4. Discontinuance of inefficient branches.
Unit banks need to operate very efficiently, or the branch will have close down due to losses.
5. Better Service
Unit banks can render efficient service to their customers. Their area of operation is limited. They can concentrate well on that limited area and provide the best possible service.
6. Close Customer-banker Relations
Since the area of operation is limited, the customers can have direct contact. Their grievances can be redressed then and there.
7. No Effects Due to Strikes or Closure
If there is a strike or closure of a unit, it does not impact the trade and industry because of its small size.
8. No Monopolistic Practices
Since the size of the bank and the area of its operation are limited, it is difficult for the bank to adopt monopolistic practices.
9. No Risks of Fraud
Due to the small size of the bank, there is stricter and closer control of management.
10. Closure of Inefficient Banks
Inefficient banks will be automatically closed as they would not satisfy their customers by providing efficient service.
11. Local Development
Unit banking is localized banking. The unit bank has the specialized knowledge of the local problems and serves the requirement of the local people in a better manner than branch banking.
12. Promotes Regional Balance
Under the unit banking system, there is no transfer of resources from rural and backward areas to the big industrial and commercial centers.
Disadvantages of Unit Banking
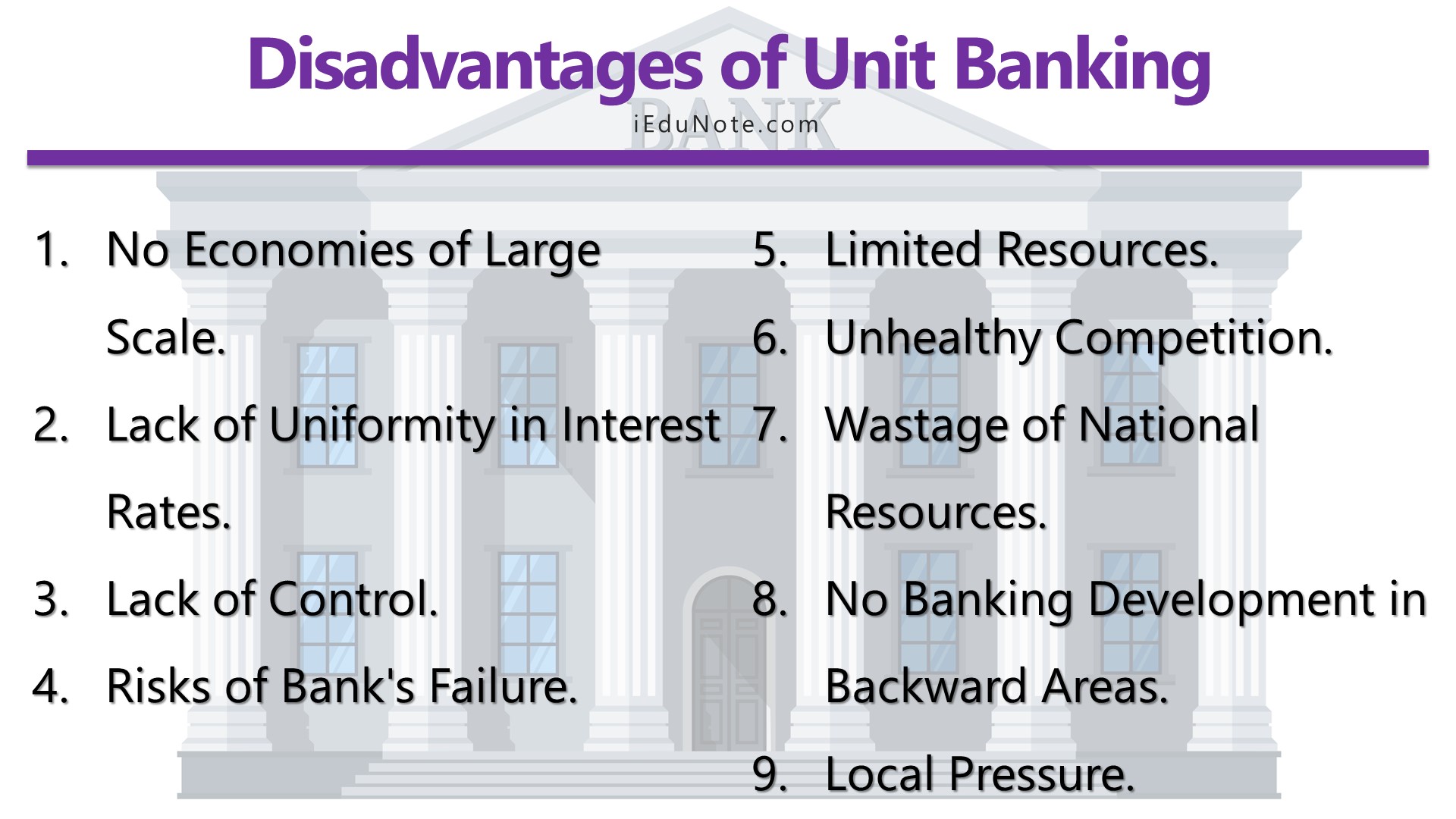
9 disadvantages of the unit banking system are;
- No Economies of Large Scale.
- Lack of Uniformity in Interest Rates.
- Lack of Control.
- Risks of Bank’s Failure.
- Limited Resources.
- Unhealthy Competition.
- Wastage of National Resources.
- No Banking Development in Backward Areas.
- Local Pressure.
1. No Economies of Large Scale
Since the size of a unit bank is small, it cannot reap the advantages of a large scale.
2. Lack of Uniformity in Interest Rates
In a unit banking system, there will be a large number of banks in operation. Transfer of funds will be difficult and costly.
3. Lack of Control
Since the number of unit banks is huge, their coordination and control would become very difficult.
4. Risks of Bank’s Failure
Unit banks are more exposed to closure risks.
5. Limited Resources
Under the unit banking system, the size of banks is small, so they cannot meet the requirements of large-scale industries.
6. Unhealthy Competition
Some unit banks come into existence at an important business center.
7. Wastage of National Resources
Unit banks concentrate in big metropolitan cities, whereas they do not have their workplaces in rural areas.
8. No Banking Development in Backward Areas
Unit banks cannot open branches.
9. Local Pressure
Since unit banks are highly localized in their business, local pressures and interferences generally disrupt their normal functioning.