In accounting, an account is a functional unit identified by an account number that serves a particular accounting purpose where one person has primary responsibility for it.
Accounts include balance sheet accounts (General Ledger (GL) Accounts) and revenue/expenditure accounts (Subsidiary Ledger (SL) Accounts).
An account is an element in an accounting system that is used to classify and summarize measurements of business activity.
Recording of transactions of similar nature relating to income, expenditure, assets, and liabilities at the end of an accounting period of a particular business under appropriate heads as per principles and rules of accounting in the condensed and classified statement is called account.
4 Types of Accounts are;
- Asset account.
- Liability account.
- Expenditure account.
- Income account.
According to the objective and the principle of the accounting equation, accounts are four types;
Asset Account
The account kept classifying the transactions for which the assets increase or decrease is called an asset account.
For example, cash account, building account, furniture account, etc.
Liability Account
The account kept classifying the transactions for which liability increases or decreases is called a liability account.
For example, creditors account, loan account, bills payable account, capital account, etc.
Expenditure Account
The account kept under different heads classifying the various expenditures of a business or institution is called an expenditure account.
For example, salary account, wage account, purchases account, etc.
Income Account
The accounts, kept under different heads having classified die transactions relating to income properly, is called income account.
For example, sale account, interest received account, rent received account, etc.
Besides the above classification according to nature accounts are also classified into the following three types;
- Personal account: The accounts relating to person and organization are personal accounts. For example, Angel Account, Jamuna and Co. Account, etc.
- Asset account, which is discussed earlier.
- Nominal or income-expenditure account: Accounts relating to income, expenditure, and losses are nominal or income-expenditure account. For example, purchase expense account, sales revenue account, salary expense account, rent expense account, etc.
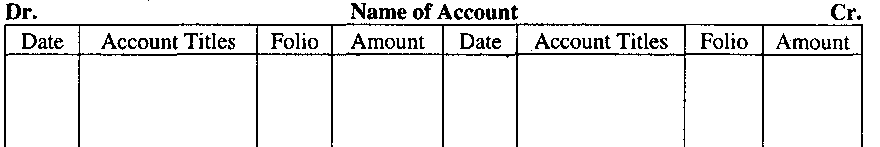
In practice, different formats of accounts are followed.
Among them, ‘T’ form and statement form are popular.
Specimens of both the formats are shown below:
‘T’ Formats:
Statement Form:
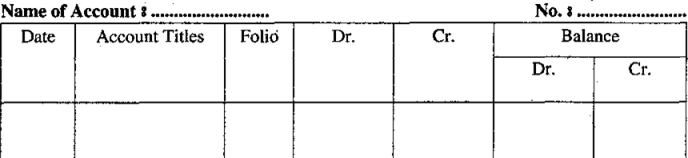
Understatement form, someone prefers to show balance in one money column instead of showing a debit balance column and credit balance column, as shown in the above format.
But this format is easy to detect whether the balance is a debit balance or credit balance.