Organizational Behavior relates to the relationship between employees and the employer in an organization.
Both are working towards the realization of the goals and objectives of any organization, and close and fruitful coordination between the two is one of the major factors towards this realization.
Organizational behavior approaches are a result of the research done by experts in this field. These experts studied and attempted to quantify research done about the actions and reactions of employees with regard to their work environments.
It is a field that has only recently begun developing, and new approaches and results are being expounded daily.
And one more approach to studying organizational behavior is the Interdisciplinary Approach.
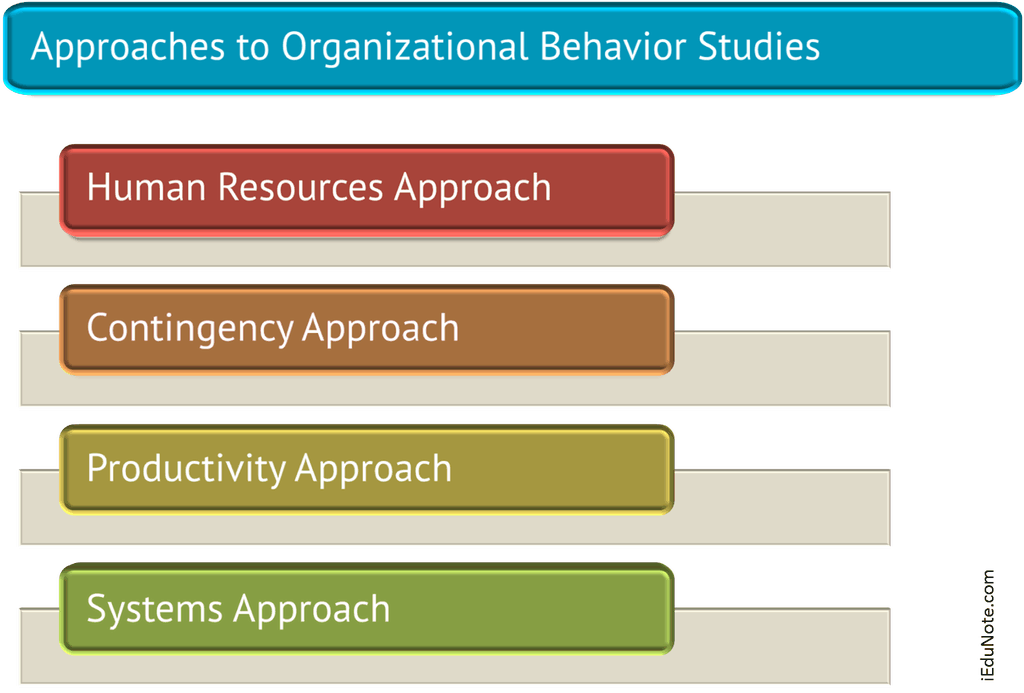
Explore the 4 approaches to organizational behavior studies: human resources, contingency, productivity, and systems approach.
Human Resources Approach
This approach recognizes the fact that people are the central resource in any organization and that they should be developed towards higher levels of competency, creativity, and fulfillment.
People thus contribute to the success of the organization.
The human resources approach is also called the supportive approach because the manager’s role changes from control of employees to active support of their growth and performance.
The supportive approach contrasts with the traditional management approach.
In the traditional approach, managers decided what employees should do and closely monitored their performance to ensure task accomplishment.
In the human resources approach, the role of managers changes from structuring and controlling to supporting.
Contingency Approach
The contingency approach (sometimes called the situational approach) is based on the premise that methods or behaviors which work effectively in One situation fail in another.
For example, Organization Development (OD) programs, the way work brilliantly in one situation but fail miserably in another situation.
Results differ because situations differ; the manager’s task, therefore, is to identify which method will, in a particular situation, under particular circumstances, and at a particular time, best contribute to the attainment of the organization’s goals.
The strength of the contingency approach lies in the fact it encourages analysis of each situation prior to action while at the same time discouraging the habitual practice of universal assumptions about methods and people.
The contingency approach is also more interdisciplinary, more system-oriented, and more research-oriented titan any other approach.
Productivity Approach
Productivity which is the ratio of output to input, is a measure of an organization’s effectiveness. It also reveals the manager’s efficiency in optimizing resource utilization.
The higher the numerical value of this ratio, the greater the efficiency.
Productivity is generally measured in terms of economic inputs and outputs, but human and social inputs and outputs also are important.
For example, if better organizational behavior can improve job satisfaction, a human output or benefit occurs.
In the same manner, when employee development programs lead to better citizens in a community, a valuable social output occurs.
Organizational behavior decisions typically involve human, social, and/or economic issues, and so productivity, usually a significant part of these decisions, is recognized and discussed extensively in the literature on OB.
Systems Approach
The Systems Approach to OB views the organization as a united, purposeful system composed of interrelated parts.
This approach gives managers a way of looking at the organization as a whole, whole, person, whole group, and the whole social system.
In so doing, the systems approach tells us that the activity of any segment of an organization affects, in varying degrees, the activity of every other segment. A systems view should be the concern of every person in an organization.
The clerk at a service counter, the machinist, and the manager all work with the people, thereby influencing the behavioral quality of life in an organization and its inputs.
Managers, however, tend to have a larger responsibility because they are the ones who make the majority people-oriented.
The role of managers is to use organizational behavior to help build an organizational culture in which talents are utilized and further developed, people are motivated, teams become productive, organizations achieve their goals, and society reaps the reward.
Inter-Disciplinary Approach
Organizational behavior is an integration of all other social sciences and disciplines, such as psychology, sociology, organizational theories, etc.
They all are interdependent and influence each other. Man is studied as a whole, and therefore, all disciplines concerning man are integrated.