What is Bank Statement?
A bank statement is a statement issued (usually monthly) by a bank describing the activities in a depositor’s checking account during the period.
A bank statement is a statement of the depositor’s bank account containing detailed deposits and withdrawals, including interest accrued and bank charges for a particular period, usually for a month.
Elements of Bank Statement
A bank statement contains the following contents;
- Depositor’s deposit for a particular period.
- Depositor’s Withdrawals or payments of cheques from his/her account by the bank for a particular period.
- Deductions from the depositor’s bank account during a particular period include a service charge, NSF (Insufficient funds), safe deposit box rent, printing cost of cheques, etc.
- Check/cheque deposit is direct into the depositor’s bank account, a deposit of a collection of notes receivable including interest, and a deposit of average interest on the deposits.
Example of Bank Statement
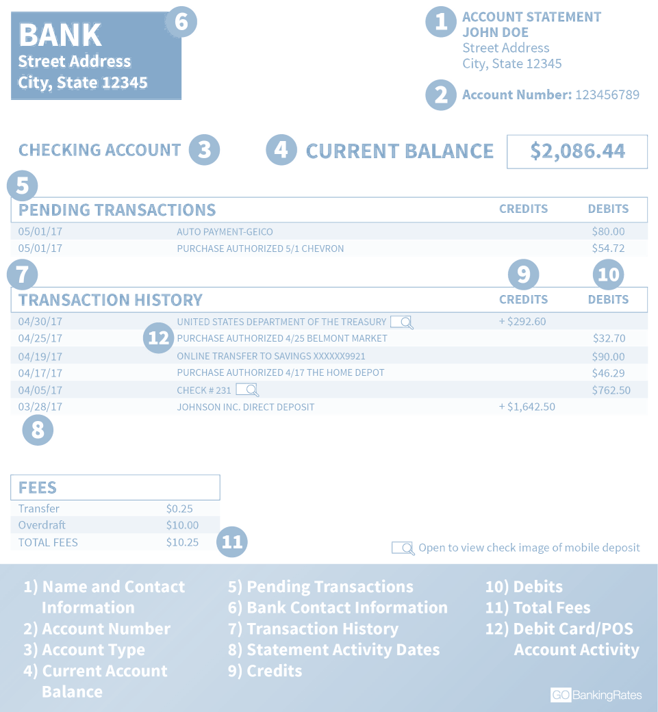
Bank Statement Format
A typical bank statement has two main parts;
- the account summary,
- transaction detail.
At the top of the first page, the account summary holds the opening balance, deposits, credits, added interest, back charges, and fees and ends with the closing balance.
The transaction detail part shows everything in chronological order, from day 1 to the last of the period—every transaction is recorded with the date, amount, and name of the payee or payer.
Debit memorandum
The bank charges a monthly fee for services rendered. The bank usually charges a fee when the average bank balance of a bank chequing account comes down to a certain required amount of money.
These fees are called bank charges, shown on the bank statement under code ‘SC.’ Bank sends a debit memorandum with the bank statement wherein the detail of bank charges is mentioned.
Credit memorandum
A depositor/account holder may direct the bank to collect his/her note receivable. The bank deposits the realized proceeds of notes receivable in the client’s bank account.
The bank sends a credit memorandum for this transaction with the bank statement. Many banks pay interest on bank chequing accounts shown in the bank statement.

