Change in demand occurs due to change in price or any of the factors other than price that were assumed constant under the law of demand. The change may be either an ‘Increase in Demand’ or ‘Decrease in Demand’ and ‘Extension in Demand’ or ‘Contraction in Demand’.
(i) Decrease and Increase in Demand:
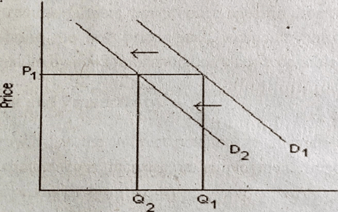
Decrease in Demand
Demand can decrease and cause a shift to the left of the demand curve for a number of reasons, including a fall in income, assuming a good is a normal good, a fall in the price of a substitute, and a rise in the price of a complement, etc.
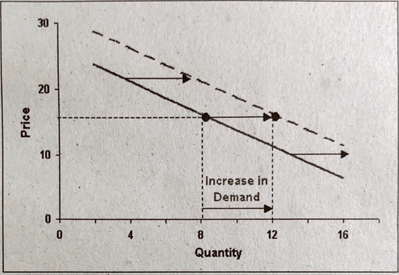
Increase in Demand
An increase in demand can be illustrated by a shift in the demand curve to the right. Increase in demand means the consumer buys more of the good at given prices than before.
For example, if the income of a consumer increases, or if the fashion for a goods increases, the consumer will buy greater quantities of the goods than before at that prices. As a result the whole demand curve will shift upward.
(ii) Extension and Contraction in Demand:
The demand for a commodity changes due to a change in price. It is called extension and contraction of demand. When there is decrease in price of commodity there is in increase in demand of that commodity.
This is called extension of demand.
When there is increase in price of a commodity there is decrease in the demand for that commodity. This called contraction of demand. Thus demand varies in opposite direction due to change in price. Downward movement on the demand curve indicates expansion of demand.
Similarly, upward movement on the demand curve indicates contraction of demand.
Extension in Demand
There is extension of demand for a commodity when there is decrease in the price of that commodity. When price is 15 Dollar the demand is 50 kilograms.
When price comes down to 10 Dollar there is extension in demand from m 50 to 60 kilograms.
{PICTURE : PAGE 82}
The diagram shows extension of demand. Quantity of demand is shown on OX axis. The price is shown on OY axis. DD is demand curve. When price comes down the quantity demanded extends and demand curve moves downward.
Contraction in Demand
There is contraction of demand for a commodity when there is increase in the price of commodity. When price is 10 Dollar per kilogram the demand is 40 kilograms.
When price increases to 20 Dollar there is contraction of demand from 40 to 30 kilograms.
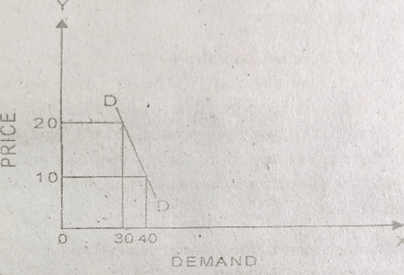
The diagram shows contraction of demand. Quality of demand is shown on the X-axis. The price is shown on the Y-axis. DD is the demand curve.
When the price increases, the quantity demanded comes down, and the demand curve moves upward.
The concept of extension and contraction of demand in economics helps us conclude that the price and demand are inversely proportional to each other.
In other words, if the price of a commodity increases, then its demand decreases, and vice versa.
Demand and Quantity Demanded:

It is important to understand the distinction between the concepts of demand and quantity demanded as they are often confused with each other
Demand represents the whole demand schedule or demand curve and shows how the price of a good is related to the quantity which the consumers are willing and able to buy, with other factors determining demand being held constant.
On the other hand, quantity demanded refers to the quantity which the consumers buy at a particular price. The quantity demanded of a good varies with changes in its price; it increases when the price falls and decreases when the price rises.
The changes in demand for a commodity occur when there is a change in factors other than price, namely, tastes and preferences of the people, incomes of the consumers, and prices of related goods.
Difference between increase/decrease of demand and extension/contraction of demand:
Demand is the quantity of a commodity demanded at a given price and given time. So, price and demand have an inverse relationship. When demand is increased by the price factor, it is called an expansion of demand. Example: sales increased due to a discount.
When it is decreased by the price factor, it is called a contraction of demand. Example: sales decreased due to an increase in price.
When the demand is increased by factors other than price, then it is called an increase in demand. Example: Sales of umbrellas increased due to seasonal demand or a lack of substitute products.
When the demand is decreased by factors other than price, then it is called a decrease in demand. Example: Sales of umbrellas decreased due to a lack of a rainy season or better substitute products available