Reliability measurement in survey situations is more difficult and less easily executed than in observational studies.
While observing a certain action over and over again, it is usually possible to repeat a survey only once. This leads to a test-retest method, which compares two tests to learn how reliable they are. The method consists of administering the test to the same group of individuals on two occasions.
Then a test-retest coefficient, sometimes referred to as a coefficient of stability, is determined. The reliability coefficient, in this instance, is simply Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient between the scores obtained by the same persons on the two administrations of the test.
Example of Test-retest Method
The test-retest method is illustrated by an example below.
Consider a group of adolescents who were asked to name a few contraceptive methods at a given time. The reported answers were recorded in numbers 0, 1,2, etc.
Later, the same group was asked the same questions and their answers were recorded exactly in the same manner.
The correlation coefficient computed from these two sets of scores provides us with a measure of stability. We illustrate this in the accompanying table, and The product-moment correlation coefficient is calculated as follows:
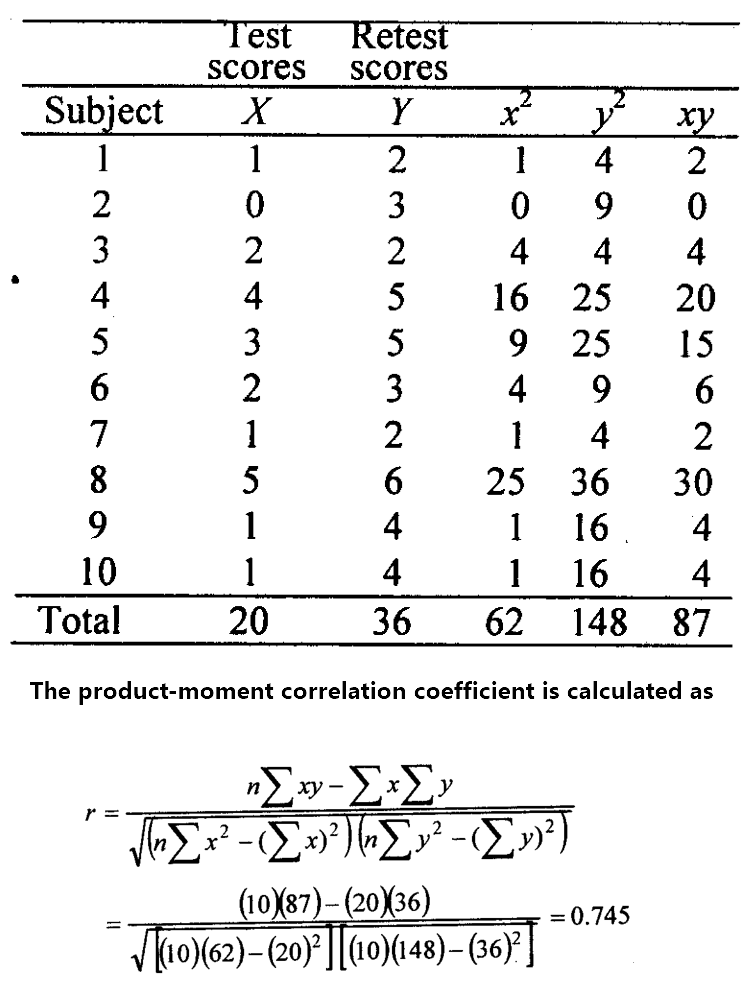
With 8 df, the Pearson r is significant at .05 (a table value of .632 is required for r to be significant). Thus, the reliability is established at .745, an acceptable value for this type of test.
The chief drawback of this method is that if the retest is given too quickly, the first test sensitizes the respondents to the topic. As a result, the respondent will remember the answers already given and repeat them.
This leads to biased reliability indicators in the upward direction.
Secondly, opinions may change from situational influences before the retest. In these cases, there is a downward bias in the stability scores.
This implies that the longer the interval between two successive administrations, the lower the correlation coefficient indicates poor reliability.
What is the primary purpose of test-retest reliability?
Test-retest reliability measures the consistency of results when the same test is administered to the same sample at different points in time. It ensures that the results of a test can be reproduced under the same conditions over time.
How is test-retest reliability calculated?
Test-retest reliability is calculated using the Pearson Correlation Coefficient between the results of the test taken at two different times. A correlation of at least 0.80 or higher typically indicates good reliability.
What is a potential bias that can affect test-retest reliability?
One potential bias is the “Practice Effect,” where participants might perform better in subsequent tests due to familiarity or practice. Another is the “Fatigue Effect,” where participants perform worse because they become mentally drained from previous tests.
How can biases like the Practice Effect be minimized in test-retest reliability?
To prevent the Practice Effect, researchers can give tests of equal difficulty but with a different variety of questions, ensuring participants can’t memorize answers from the first test.
What is interrater reliability?
Interrater reliability measures the degree of agreement between different people observing or assessing the same thing. It helps ensure that multiple researchers or observers rate or score a variable consistently.
What is parallel forms reliability?
Parallel forms reliability measures the correlation between two equivalent versions of a test. It’s used when there are multiple versions of a test designed to measure the same thing.
How is internal consistency assessed?
Internal consistency measures the correlation between multiple items in a test intended to measure the same construct. It can be calculated using methods like average inter-item correlation or split-half reliability.