Both transactional and transformational leadership are needed. Transactional leaders ensure that routine work is done reliably, while transformational leaders look after initiatives that add value.
Creating a high-performance workforce has become increasingly important, and to do so, business leaders must be able to inspire organizational members to go beyond their task requirements.
As a result, new leadership concepts have emerged; transformational leadership is one of them. In many organizations, both transactional and transformational leadership are needed.
The transactional leaders (or managers) ensure that routine work is done reliably, while the transformational leaders look after initiatives that add value.
Transactional leaders handle all the details that come together to build a strong reputation in the marketplace while keeping employees productive on the front line.
Transformational leadership styles are crucial to the strategic development of a small business.
Small businesses with transformational leaders at the helm shoot for ambitious goals, and they can achieve rapid success through the vision and team-building skills of the leader.
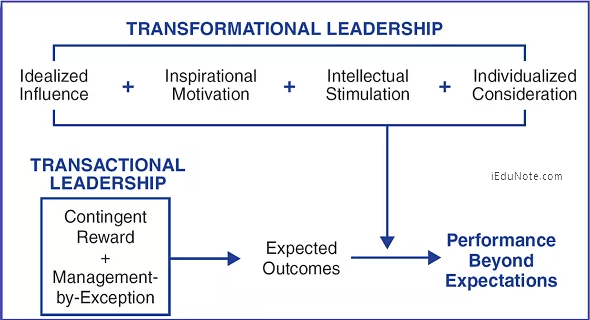
Difference Between Transactional and Transformational Leadership
Transactional and transformational are the two modes of leadership that tend to be compared the most.
James MacGregor Burns distinguished between transactional leaders and transformational by explaining that: a transactional leader is a leader who exchanges tangible rewards for the work and loyalty of followers.
Transformational leaders engage with followers, focus on higher-order intrinsic needs, and raise consciousness about the significance of specific outcomes and new ways in which those outcomes might be achieved.
Transactional leaders tend to be more passive as transformational leaders demonstrate active behaviors, including providing a sense of mission.
| Transactional Leadership | Transformational Leadership |
|---|---|
| Leadership is responsive | Leadership is proactive |
| Works within the organizational culture. | Works to change the organizational culture by implementing new ideas. |
| Employees achieve objectives through rewards and punishments set by the leader. | Employees achieve objectives through higher ideals and moral values. |
| Motivates followers by appealing to their self-interest. | Motivates followers by encouraging them to put group interests first. |
| Management-by-exception maintain the status quo; stress correct actions to improve performance. | Individualized consideration Each behavior is directed to each individual to express consideration and support. |
| Intellectual stimulation or motivation is zero. | Intellectual stimulation Promote creative and innovative ideas to solve problems. |