What is the Cash Book?
Cash Book contains cash transactions passing into and out of business. 2 types of Cash Book are (1) general cash book and (2) petty cash book. The general cash book is subdivided into the single column, double column, and treble column cash book.
The primary book where transactions regarding cash receipts and payments are recorded in chronological order of dates with explanations and balance is drawn at the end of the day or a particular period is called cash book.
Among the financial transactions of concern, cash transactions carry much more importance.
That’s why these are recorded in a separate book of account.
Since all cash transactions are recorded in this book in the ledger account format, a separate cash account in the ledger is not needed.
Cash Book Example
The owner can know the accurate cash position of his business from the cash book. ‘T’ form cash book contains two sides: the left-hand side means the debit side, and the right-hand side means the credit side.
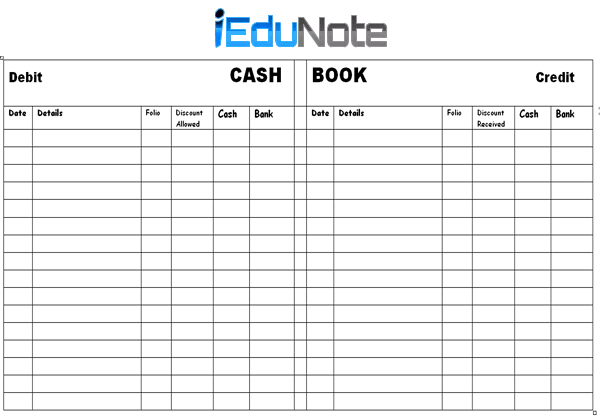
The debit side stands for cash receipts, and the credit sides stand for cash disbursements.
All the receipts are recorded on the receipt sides, and all cash disbursements are recorded on the payment side of the cash book.
At the end of the day or a particular period, the totals of receipts and payments are made, and the difference between these two totals is shown as balance.
This balance indicates the amount of cash in the hand of an organization.
Cash Book is a book in which an account is kept of the receipts and disbursements of money.
Importance of Cash Book
The features of the cash book are as follows;
- Since only cash transactions are recorded in the cash book, it is a special journal.
- The cash book serves the purpose of the journal and ledger.
- The cash book always shows a debit balance.
- The balance of the cash book always means cash in hand. The balance of the cash book and cash of a cash box must be equal.
- Non-cash transactions of cash books are transferred to a relevant account in the ledger.
Cash Book is both a Journal and a Ledger
Some accountants term cash book as a journal and some others term it as a ledger. Modem accountants term cash book both as journal and ledger.
Cashbook is a journal; because:-
- After the transactions, these are recorded in the cash book in chronological order of dates with explanations like a journal.
- How transactions are posted into the ledger from the journal is followed in the case Of posting transactions to the ledger from the cash book.
- As separate special journals are maintained for various transactions, cash book is similarly maintained for cash transactions.
- Cash transactions are recorded in the cash book according to debit and credit.
- Other than cash book, no subsidiary journal is maintained for cash transactions.
For all these features of the cash book, it is called a journal.
Cashbook is a ledger; because:-
- The format of the cash book is similar to that of a ledger account.
- Like a ledger account, the cash book consists of two sides – the debit side and the credit side if prepared in ‘T’ format.
- Like ledger accounts, the balance of the cash book is determined and transferred to the trial balance.
- The cash book serves the purpose of the cash account. In such a case, the cash account is not prepared in the ledger.
The cash book is called a ledger because of its above-mentioned characteristics. It is very much evident from the above discussion. Cash book is both journal and ledger as it contains all journal and ledger features and serves purposes of both.
Advantages of Cash Book
- Cash receipts and cash payments for a particular period can easily be ascertained from the cash book.
- Since cash transactions are recorded in the cash book, it becomes convenient to find any cash transactions for future reference.
- It avoids the journalization of huge cash transactions.
- The amount of cash in hand can be ascertained at any time, and it can be compared with the cash in a cash box. This ensures the accuracy of the cash book and detects »misuse or misappropriation of cash.
- Cashbook minimizes time and labor in preparing the ledger as it performs both the journal and ledger functions.
- Proper maintenance of the cash book influences the cashier’s morality, which refrains him from stealing cash.
For proper maintaining of cash books, preventive measures are taken to avoid fraud and forgery.
For example;
The officials entrusted with preparing cash books are seated in a separate room, and the entrance of unauthorized employees is restricted there.
Types of Cash Book

Generally, a cash book is of two types –
- General cash book.
- Petty cash book.
3 types of general cash books are detailed.
- Single column cash book,
- Double column cash book,
- Treble column cash book.

1. Double Column Cash Book
The cash book containing two money columns – cash column and bank column on both sides for recording cash and bank transactions is called a double column cash book.
All cash receipts and all bank deposits are recorded on the debit side, and all cash payments and all payments through cheques are recorded on the credit side of this cash book.

Cash receipts are recorded in the cash column of the debit side, and cash payments are recorded in the cash column of the credit side. Cash and cheques deposited in the bank are recorded in the bank column of the debit side, and payment by cheques are recorded in the bank column of the credit side.
The debit balance of the double column cash book indicates cash in hand and cash at the bank of a particular date of concern.
There might be a credit balance of the bank column, indicating bank overdraft or excess withdrawn over deposits.
Method of Preparing Double Column Cash Book
Preparing a double column cash book is almost similar to that of the single column cash book. The double-column cash book system has been introduced to avoid complexity in posting bank transactions in the single column cash book.
Here all bank transactions are directly recorded in bank columns.
When preparing a double column cash book, it is to be kept in mind that all types of cash receipts are to be recorded in the cash column of the debit side, and all bank deposits are to be recorded in the bank column of the debit side.
On the other hand, cash payments are recorded in the cash column of the credit side, and payments through cheques are recorded on the debit side.
2. Treble Column Cash Book
The cash book containing three money columns on both sides is called a treble column cash book. The columns are ‘Cash,’ ‘Bank,’ and ‘Discount.
In a treble column cash book, there are three money columns on both sides for recording transactions relating to cash, bank, and discount.

Like the double column, cash book cash receipts and bank deposits are recorded in the debit cash column and bank column respectively of the treble column cash book, and cash payments and payment by cheque are recorded in the credit cash column and bank column, respectively.
The discount allowed to the customer for realizing debits is recorded in the debit discount column of the treble column cash book, and discount received from suppliers or creditors in making a payment is recorded in the credit discount column of the treble column cash book.
In preparing a treble column cash book, it must be carefully noted that discount columns need not be balanced.
The total debt discount column and the total credit discount column are treated as separate balances.
The total debt discount column means expense, and the total credit discount column means income.
Advantages of Treble Column Cash Book
The advantages of treble column cash book are stated below,
- Time and labor-saving A good deal of time and labor are saved because for maintaining a treble column cash book cash account, bank account, and discount accounts are not needed to be prepared in the ledger.
- Knowing cash and bank balance Cash and bank balances can easily be ascertained whenever needed from a treble column cash book.
- Knowing discount income and discount expense, the discount income, and discount expenses can easily be known from the total credit discount column and debit discount column of the treble column cash book.
3. Petty Cash Book
Companies maintain two types of Petty Cash Book for all cash transactions of a business.
- Columnar petty cash book
- Imprest petty cash book.
The Book Containing the record of all cash passing into and out of business is called the Cash Book.





